Vaccine Information
The JYNNEOS mpox vaccine is recommended for people who have been exposed to mpox and people who may be more likely to get mpox. If you are a close contact of a confirmed mpox case, please reach out to your local health department and or provider. Post-exposure prophylactic vaccination must be given within 14 days of exposure.
A required second dose should be received 4-5 weeks after the first vaccine dose. The immune response takes 14 days after the second dose to reach maximum strength. People who get vaccinated should continue to take steps to protect themselves from infection by avoiding close, skin-to-skin contact, including intimate contact, with someone who has mpox.
Contact your healthcare provider, local pharmacy, or local health department for mpox vaccine availability.
Information for the Public
CDC Mpox Website
Social Gatherings, Safer Sex and Mpox - CDC
Frequently Asked Questions
- What are the signs and symptoms of mpox?
Symptoms of mpox can start with:
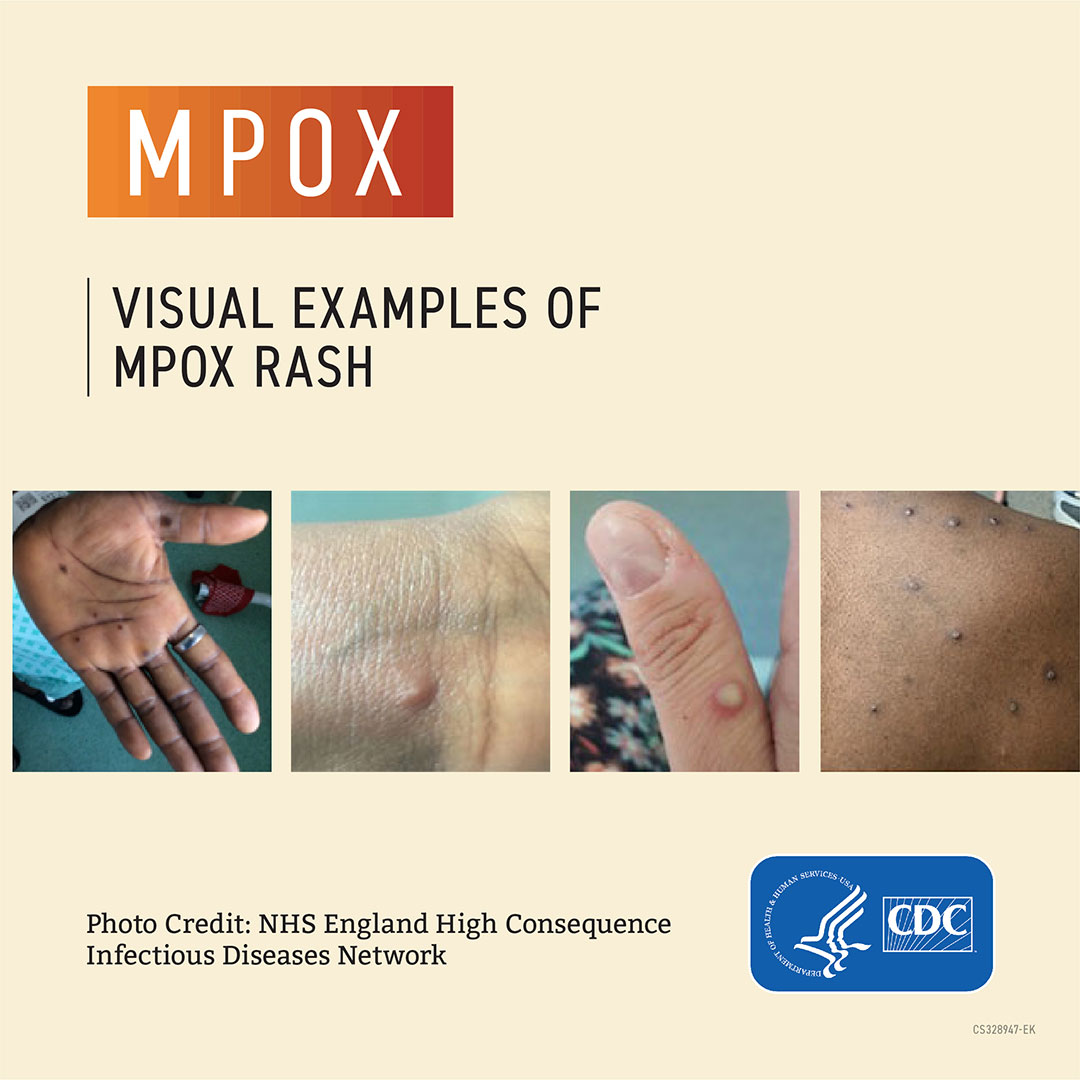
- Fever, headache, muscle aches and backache, swollen lymph nodes, chills, exhaustion
These symptoms usually appear within 3 weeks after someone is exposed to mpox. About 1-4 days later, a rash that can look like pimples or blisters appears, usually on the face, inside the mouth, and on other parts of the body, like the hands, feet, chest, genitals, or anus.
The rash goes through different stages before healing completely. The illness typically lasts 2-4 weeks.
Sometimes, people get a rash first, followed by other symptoms. Others only experience a rash.
- If I was exposed, when should I expect to see symptoms?
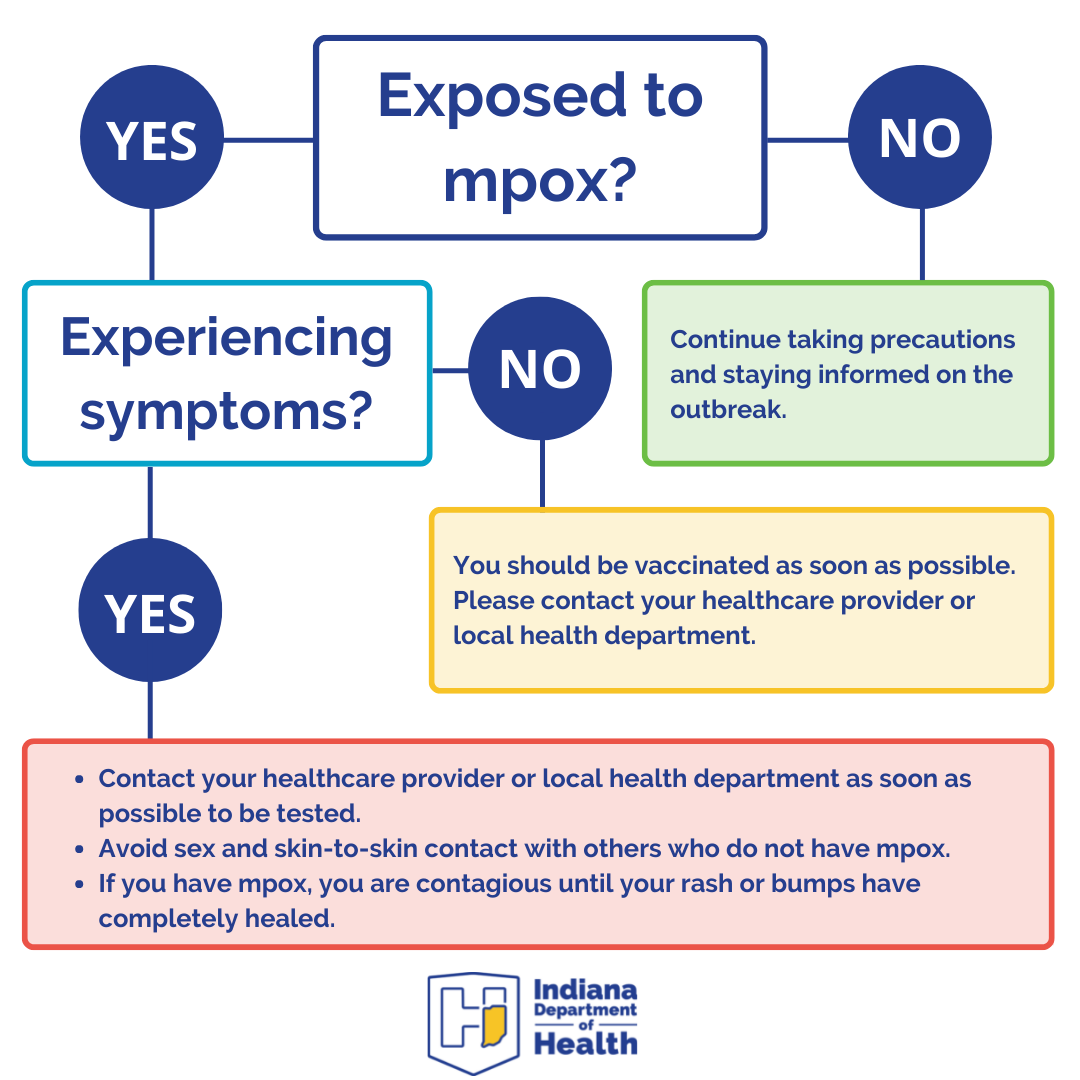
Symptoms usually appear 7-14 days after exposure but can occur up to 21 days after exposure.
If you know that you have been exposed (close physical contact) to a person who had symptoms of mpox at the time of your exposure, you should contact your healthcare provider as you may be eligible for a post-exposure prophylaxis vaccine. Receiving the vaccine within 4 days of exposure can prevent infection and within 14 days of exposure can reduce symptoms.
You need to watch for symptoms, and if a rash develops, isolate and then seek medical attention for evaluation and testing.
If you are a close contact of a confirmed mpox case, please reach out to your local health department and or provider. Post-exposure prophylactic vaccination must be given within 14 days of exposure.
- How does mpox spread?
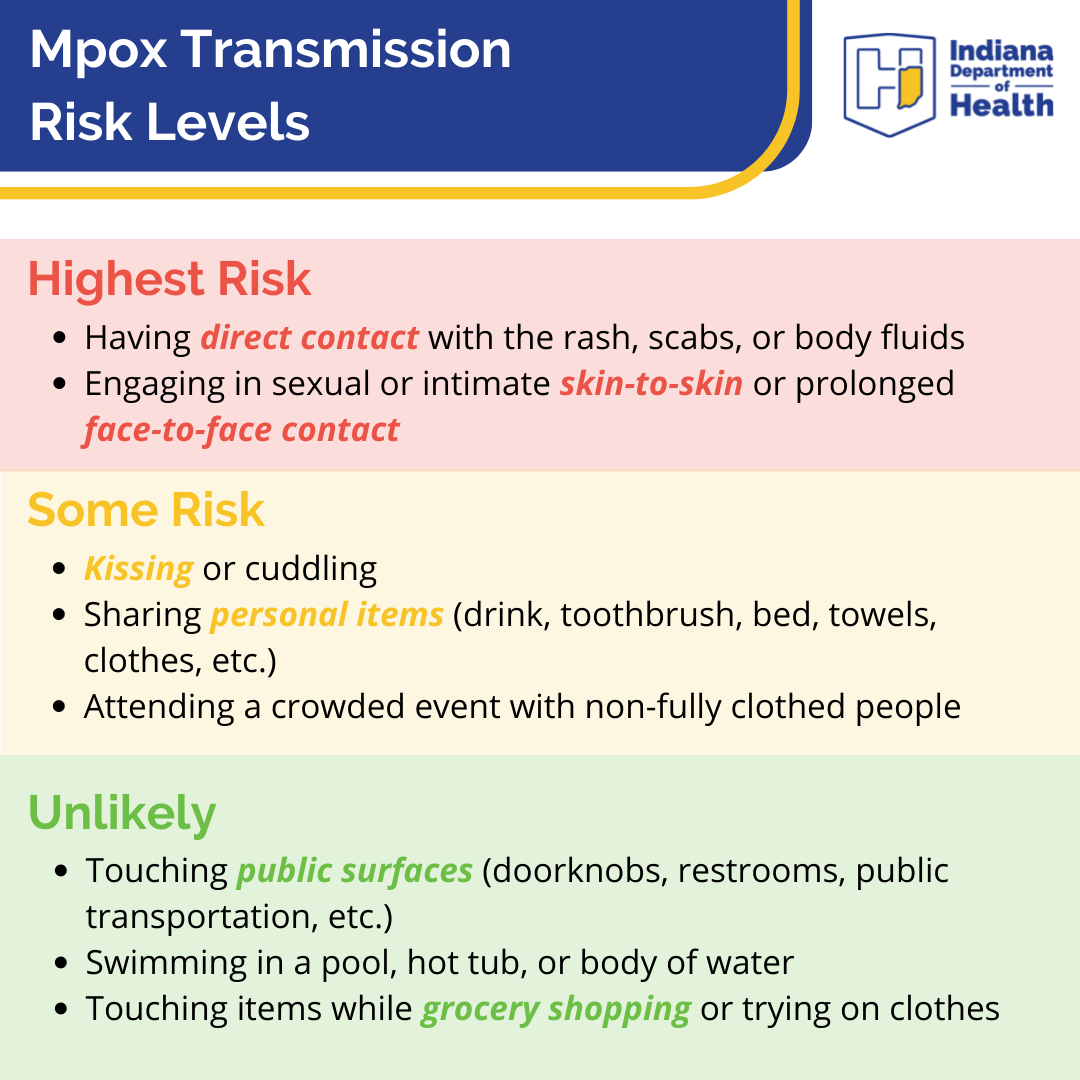
Mpox can spread to anyone through close, personal, often skin-to-skin contact, including:
- Direct contact with mpox rash, scabs, or body fluids from a person with mpox.
- Touching objects, fabrics (clothing, bedding, or towels), and surfaces that have been used by someone with mpox.
- Contact with respiratory secretions.
A person with mpox can spread it to others from the time symptoms start until the rash has fully healed and a fresh layer of skin has formed. The illness typically lasts 2–4 weeks.
Protect yourself from getting mpox:
- Avoid close, skin-to-skin contact with people who have a rash that looks like mpox.
- Avoid contact with objects and materials that a person with mpox used.
- Wash your hands often.
Someone who has mpox can spread infection to others from the time symptoms start until the rash has fully healed (scabs have fallen off) and a fresh layer of skin has formed. The illness typically lasts 2-4 weeks. People who do not have mpox symptoms cannot spread the virus to others. At this time, it is not known if mpox can spread through semen or vaginal fluids.
Here's guidance from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention about how to clean at home.
- Who is at risk for mpox infection?
Anyone with a rash that looks like mpox should talk to their healthcare provider, even if they don’t think they had contact with someone who has mpox. People who may be at higher risk might include, but are not limited to, those who:
- Had contact with someone who had a rash that looks like mpox or someone who was diagnosed with confirmed or probable mpox
- Had skin-to-skin contact with someone in a social network experiencing mpox activity; this includes men who have sex with men who meet partners through an online website, digital application (“app”), or social event (e.g., a bar or party)
- Traveled outside the U.S. to a country with confirmed cases of mpox or where mpox activity has been ongoing
- Had contact with a dead or live wild animal or exotic pet that exists only in Africa or used a product derived from such animals (e.g., meat, creams, lotions, powders, etc.)
- Where do I go to get tested for mpox?
Call your healthcare provider. They can set up an appointment for testing or direct you to where you can be tested. If you do not have a provider and you have a rash or symptom that you are concerned about, you may go to an urgent care or emergency department for care and evaluation.
Information for Clinicians
Clinical Guide for Mpox Testing, Specimen Collection and Submission (printable) - updated 10/26/23
Frequently Asked Questions
- How do patients present with mpox?
Patients with a new characteristic rash or who meet one or more of the epidemiologic criteria and in which there is a high suspicion should be tested for mpox.
Risk Factors
Mpox spreads between people primarily through direct contact with infectious sores, scabs, or body fluids. It can also spread by respiratory secretions during prolonged, face-to-face contact. People who may be at higher risk might include, but are not limited to, those who within 21 days of illness onset:
- Had contact with someone who had a rash that looks like mpox or someone who was diagnosed with confirmed or probable mpox
- Had skin-to-skin contact with someone in a social network experiencing mpox activity;
- Traveled outside the United States to a country with confirmed cases of mpox or where mpox activity has been ongoing
- Had contact with a dead or live wild animal or exotic pet that exists only in Africa or used a product derived from such animals (e.g., game meat, creams, lotions, powders, etc.)
- How do I collect and submit specimen for testing?
Materials Needed for Collection and Handling Instructions - CDC
How to Collect Specimen and Protect Clinical Staff - CDC
Several commercial labs are now testing for orthopox virus which detects mpox. Please work with your lab staff to send specimen to these commercial labs: Aegis Science, Labcorp, Mayo Clinic Laboratories, Quest Diagnostics and Sonic Healthcare. Results will be transmitted to the IDOH. Prior IDOH authorization is not required to submit specimens to commercial laboratories.
If you are unable to submit to one of these five labs, you may submit a specimen for testing through the Indiana Department of Health (IDOH)
Specimens should be submitted via LimsNet, an online system that will make results available as PDF files the minute they are released at IDOH Laboratories. Specimens should be submitted through the Biothreat submission page in LimsNet. To get a free LimsNet account established at your facility for electronic submission and results reporting, call the help desk at (317) 921-5506 or email LimsAppSupport@health.in.gov.
Mpox Specimen Submission Instructions - IDOH (updated 8/10/22)
Mpox Virus Testing Considerations Prevent False Positive Test Results - CDC - What should I tell my patient about home isolation, contact tracing and contact monitoring?
Home Isolation Guidance - CDC
Contact the local health department for wraparound services to individuals in isolation.Notifying Close Contacts - CDC
Contact the local health department for assistance with contact tracing. - Mpox Vaccination Information
JYNNEOS is a third-generation vaccine based on a live, attenuated orthopoxvirus, Modified Vaccinia Ankara (MVA). MVA is a live virus that does not replicate efficiently in humans. JYNNEOS is known internationally as Imvamune® or Imvanex®; it is manufactured by Bavarian Nordic. It is fully licensed in the U.S. for subcutaneous administration in individuals 18 years of age and older. As of April 1, 2024, JYNNEOS is commercially available in the U.S.
- JYNNEOS Vaccine Guidance (CDC)
- JYNNEOS Intradermal Administration
- JYNNEOS Cheat Sheet
- JYNNEOS Healthcare Provider Fact Sheet
- JYNNEOS Storage and Handling
- After vaccination palm card for patients (English and Español)
Pre-exposure Prophylaxis
- People at risk of mpox should ideally be vaccinated prior to exposure to monkeypox virus (MPXV).
- Two vaccines may be used for the prevention of mpox:
- JYNNEOS vaccine is approved and recommended by CDC and ACIP for the prevention of mpox and smallpox. During the ongoing clade II MPXV outbreak (i.e., outbreak that began in 2022 affecting predominantly gay, bisexual, and other men who have sex with men), JYNNEOS has been the main vaccine used in the United States.
- ACAM2000 vaccine is approved for immunization against smallpox and could be made available for use against mpox under an Expanded Access Investigational New Drug (EA-IND) protocol. In the United States, there is a large supply of ACAM2000, but this vaccine has more known side effects and contraindications.
- The standard regimen for JYNNEOS involves a subcutaneous (Subcut) route of administration with an injection volume of 0.5mL. An alternative regimen involving intradermal (ID) administration with an injection volume of 0.1mL may be used under an Emergency Use Authorization (EUA).
- Both the standard (0.5mL Subcut) and the alternative (0.1mL ID) regimen have been found to be effective for mpox prevention.
- There is currently adequate supply of JYNNEOS vaccine. Therefore, clinicians can preferentially administer JYNNEOS via the subcutaneous route.
- JYNNEOS vaccine is licensed as a series of two doses administered 28 days (4 weeks) apart.
- For people with sexual risk factors for mpox who have not been diagnosed with mpox during the ongoing outbreak or have not already received 2 doses of the JYNNEOS vaccine, CDC routinely recommends vaccination.
- Administration of additional JYNNEOS vaccine doses (more than 2 doses) is currently not recommended.
- For those at occupational risk of exposure to orthopoxviruses (e.g., certain research laboratorians*) a booster is recommended at 2-10 years depending on the type of work being performed.
- People who are vaccinated should continue to take steps to protect themselves from infection by avoiding close, skin-to-skin contact, including intimate contact, with someone who has mpox.
Post-exposure Prophylaxis
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommends post-exposure prophylaxis for high or intermediate risk contacts of mpox cases.
JYNNEOS (also known as Imvamune or Imvanex) is licensed by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for preventing mpox infection. The sooner an exposed person gets the vaccine, the better. CDC recommends that the vaccine be given within 4 days from the date of exposure to prevent onset of the disease. If given 4–14 days after the date of exposure, vaccination may reduce the symptoms of disease but may not prevent the disease.
Quick Reference Guide to Post-exposure Prophylaxis
Clade I Mpox Considerations
- CDC has vaccination recommendations for people traveling to countries with clade I outbreaks.
- As of December 11, 2024, these countries include Burundi, Central African Republic, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Republic of the Congo, Rwanda, and Uganda.
- The risk of clade I mpox to the general public in the U.S. remains low.
For the most up to date information concerning the clade I mpox outbreak please visit the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
- How do I get TPOXX for treatment?
Treatment
Tecovirimat (also known as TPOXX or ST-246) is FDA-approved for the treatment of human smallpox disease caused by Variola virus in adults and children. However, its use for other orthopoxvirus infections, including mpox, is not approved by the FDA. Therefore, CDC holds a non-research expanded access Investigational New Drug (EA-IND) protocol that allows for the use of tecovirimat for primary or early empiric treatment of non-variola orthopoxvirus infections, including mpox, in adults and children of all ages.
Patients should contact their providers to inquire about obtaining TPOXX for treatment.
A unique survey entry must be completed for each individual TPOXX request.
The National Institutes of Health (NIH)-sponsored Study of Tecovirimat for Mpox (STOMP) clinical trial has been concluded. For adults without severe immunocompromise or severe disease and who are not pregnant or lactating, STOMP enrollment was the only route of access to oral tecovirimat. NIH closed STOMP enrollment based on the interim analysis at 75% of the randomized study’s target enrollment that showed no difference in the time to lesion resolution between tecovirimat-treated participants to those who received placebo. Please refer to the NIH’s announcement on December 10, 2024, for further details.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) has also posted updated information regarding tecovirimat on Tecovirimat (TPOXX) for Treatment of Mpox and Clinical Treatment of Mpox.
- What are the recommendations for healthcare personnel?
Treatment Information for Healthcare Professionals - CDC
If a probable case (orthopox positive) is identified, IDOH will report the result to the clinician and facilitate a consultation call with CDC and the clinician for treatment assessment and ordering. - What should I do with expired TPOXX?
- Once your bottles/vials of TPOXX expire, please check ASPR for extensions that have been given. These are listed by lot number.
- Once you have verified that it is expired, dispose of the medication in the same manner that your location uses for all expired medications.
- What is the current situation with the Clade I mpox outbreak overseas?
The World Health Organization has identified a significant outbreak of mpox (Clade I) in the Democratic Republic of Congo, with limited spread to other countries. This outbreak involves a variant of mpox (Clade I) different from the one circulating in the U.S. (Clade II). Clade I mpox is more infectious and associated with more severe illness compared to Clade II. Currently, there have been no reported cases of Clade I mpox in the U.S. The JYNNEOS vaccine provides protection against both Clade I and Clade II mpox.
Information for Local Health Departments
If a local health department has a suspected or confirmed case of mpox please contact your regional DIS. You can find contact information on the DIS Contact Map located at https://www.in.gov/health/hiv-std-viral-hepatitis/std-surveillance/
Additional Resources
CDC HAN (Health Alert Network) Health Update - Mpox Caused by Human-to-Human Transmission of Monkeypox Virus in the Democratic Republic of the Congo (8/7/24)
Mpox in 2022 - What Clinicians Need to Know - Jeannette Guarner, MD, Carlos del Rio, MD and Preeti N. Malani, MD, MSJ (6/13/22)
Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System (VAERS)
Indiana Health Alert Network Advisory, Mpox - IDOH (6/10/22)
Clinical Guidance (CDC)
Clinical Considerations for Mpox in People Who are Pregnant or Breastfeeding (CDC)
Clinical Considerations for Mpox in Children and Adolescents (CDC)