Transportation Systems Management Operations (TSMO) at INDOT
Transportation Systems Management Operations (TSMO) at INDOT
Transportation Systems Management Operations (TSMO) is a set of strategies that focuses on operational improvements to maximize the efficiency and safety of existing transportation systems. Strategies are implemented to get the most performance out of existing transportation facilities. This improves system reliability for motorists.
TSMO integrates planning and design with operations and maintenance to manage and operate a transportation system. Data, technology and collaboration are used to optimize system mobility and reliability and improve the driver experience. Improvements are typically deployed as a set of flexible strategies that can be used throughout a corridor.
TSMO strategies can be particularly effective in urban areas where space is at a premium. In some instances, TSMO strategies can be an alternative to added capacity by increasing the mobility and reliability of the existing system. INDOT is examining where to employ TSMO strategies across the state to improve safety and flow while maximizing resources.
Key Benefits of TSMO
- Safety
- Reliability
- Efficiency
TSMO reduces crashes and fatalities, optimizes travel times in critical corridors and implements strategies to optimize the capacity of the existing transportation system and alleviate congestion. Other benefits include increased fuel economy, cleaner air, and the more efficient use of resources -- both funding and facilities. TSMO helps to balance supply and demand of the transportation system.
Proven: TSMO strategies are successfully in use across the country and the region, including on the Indiana Toll Road, the Illinois Tollway, around Chicago, and along US 23 in Michigan.
Examples of TSMO Strategies
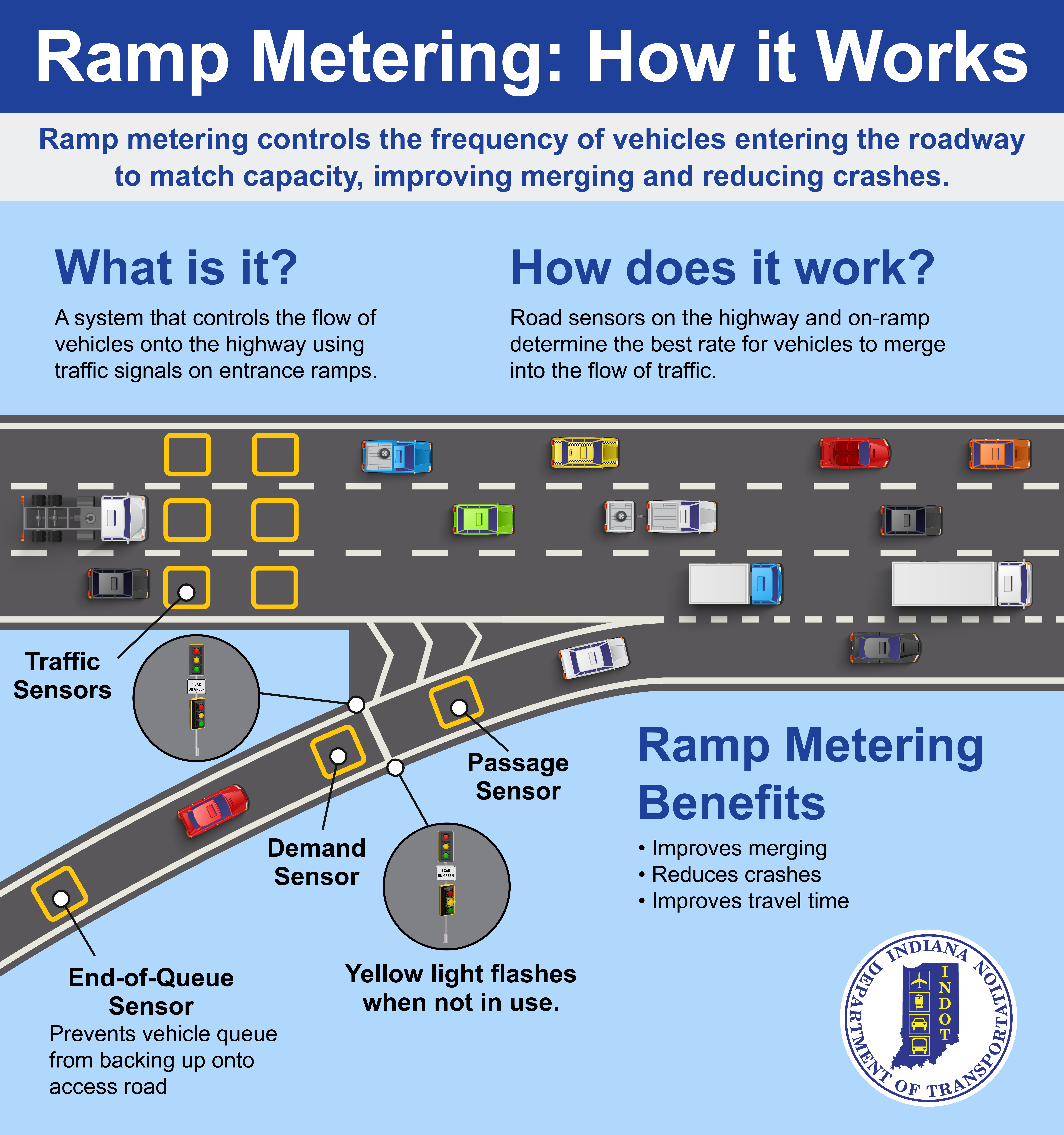
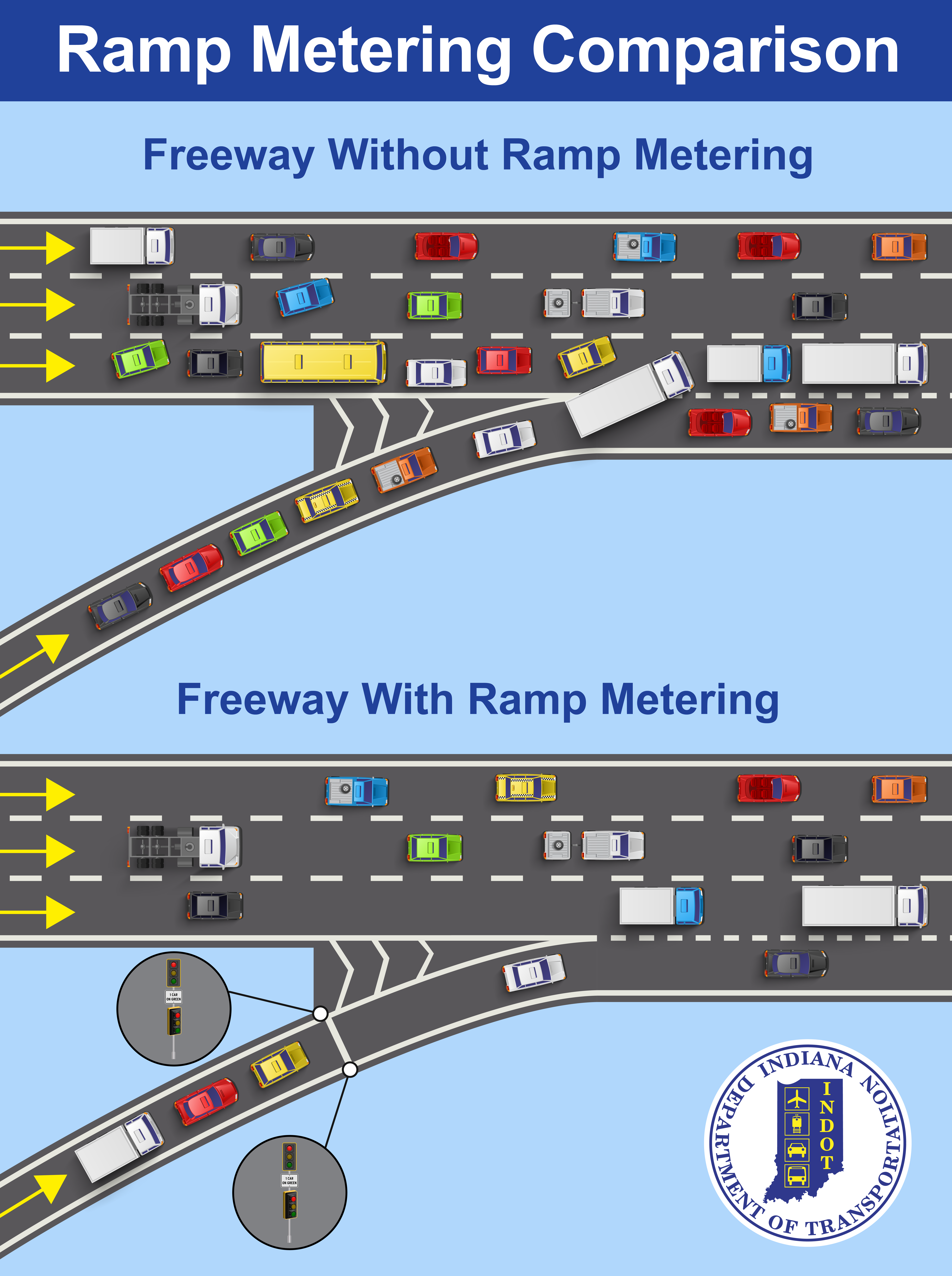
- Ramp metering controls the frequency of vehicles entering the roadway to match road capacity, leading to improved merging and reduced crash rates.
- Traffic signals are installed at on-ramps to control vehicles entering the roadway.
- Use of signals helps break up packed lines of traffic on the roadway.
- Reduces crash rates, improves travel time, and improves traffic speed and reliability.
- Variable Speed Limits (VSLs) adjust based on real-time traffic, roadway incidents, work zones, and weather conditions to reduce crash frequency and severity.
- Dynamic Shoulder Lanes use the shoulders for additional capacity during peak congestion or in response to incidents.
- Improved Signage increases driver knowledge and awareness of current traffic conditions, helping to reduce crashes and keep motorists informed.
- Dynamic Lane Control includes opening or closing individual traffic lanes based on current conditions using signals above each lane.
- Queue Warning uses real-time displays of messages to alert drivers to slowdowns ahead, reducing the potential for rear-end crashes and secondary crashes.
- Event Management reduces congestion by improving operation and maintenance practices. Examples could include incentivizing tow companies to quickly remove disabled vehicles or increasing Hoosier Helper staff.